Inflammation of the tissues of the prostate is quite common, in men the causes of inflammation of the prostate are infections and congestion. According to statistics, after 30 years, 30% of men already suffer from this disease, and as they age, their numbers increase and the disease becomes younger. As far as you know, prevention is the best treatment, and if we know the causes of a particular pathology, we can more easily protect ourselves from it.
Where does prostatitis come from?
The clinical picture of the disease may contain different symptoms. The most common and significant are urinary tract disorders and sexual dysfunctions. The totality of the symptoms and the extent of their manifestation in each case depend on the individual characteristics of the man, in particular his lifestyle, general state of health and the work of the immune system.

According to the reasons, two forms of the disease are usually distinguished:
- infectious
- pangó.
Causes of infectious prostatitis
The infectious form of the disease of prostatitis is caused by pathogenic microorganisms. In this case, the disease develops when the focus of the infection is formed in the prostate. It can occur in both acute and chronic forms, but infectious prostatitis is more often acute. At the same time, the general well-being of the man deteriorates, there are pains in the lower back, in the groin, the urination process is disturbed, and the body temperature rises.
Acute prostatitis
In men, the direct causes of prostatitis are foci of infection that can be located in completely different organs. Pathogens enter the prostate either by rising from the rectum or urethra or by landing through the blood and lymph.
The most common pathogens of acute prostatitis are:
- Colibacillus,
- Staphylococcus aureus,
- Streptococcus,
- Gonococcus.
What causes prostatitis, where are the foci of infection that lead to acute prostatitis? Above all, urological infections, sexually transmitted diseases, upper respiratory diseases, intestinal infections can cause inflammation of the prostate. Even banal tooth decay can provoke the development of prostatitis because there is an infection in the carious teeth.
The ascending pathway for the spread of pathogenic microorganisms enters the tissues of the prostate from the rectum and urethra. When does this happen? Most often, this phenomenon is due to urological infections: cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis. Possible causes of prostatitis are sexually transmitted diseases, of which gonorrhea is the most common. When a man becomes ill with this disease, a focus of infection is formed in him, which is located near the prostate. This means that the pathogenic microflora can easily spread to prostate tissue. Gonococcus or Trichomonas can also enter the prostate gland during unprotected intercourse if the partner is ill.
The descending pathway for the infection to spread involves penetrating the organs above the prostate through the blood or lymph. In this case, the causes of prostatitis lie in the negative effects of infections of the throat, upper respiratory tract or oral cavity on the body. Diseases that cause prostatitis can include bronchitis, influenza, tonsillitis, and tuberculosis. The resulting prostatitis is usually a complication, and the first symptoms appear a few weeks after the underlying infection.
It plays an important role in whether or not inflammation occurs, the state of immunity. Not all men with foci of infection develop prostatitis. When the body is in an active, strong state, immunity copes with the infection and the pathological process stops. Deterioration of the state of defense leads to the development of complications. They manifest in a variety of diseases, all of which depend on individual characteristics and "weak points" in the body. The prostate gland is one of the most sensitive organs in the male body, so any negative effects can affect its condition.
Why is immunity declining? The reasons for this are stress, malnutrition, sedentary lifestyle, hypothermia. Infections themselves, especially sexually transmitted infections, become a factor in the reduction of immunity and contribute to the development of complications.
Chronic prostatitis
In the acute form of the disease, all the symptoms are quite clear, it is impossible not to pay attention to them, so men with acute prostatitis usually seek medical attention immediately. The chronic form of the disease is slow, the symptoms are not very pronounced, the state of health usually remains satisfactory, the temperature is normal. It is due to the low syndrome of chronic prostatitis that it is so prevalent. Men do not tend to actively treat problems that do not have vivid, characteristic symptoms, so they usually do not rush to the doctor with mild manifestations of prostatitis.
What causes chronic prostatitis? The causes may be the same as in acute prostatitis, but due to the work of the immune system or the weakness of the pathogenic microflora, the disease does not become acute but develops slowly. However, the cause of chronic prostatitis is most often an acute form of the disease that has not been treated effectively enough.
Reasons for the transition from acute to chronic prostatitis:
- Late start of treatment,
- Bad start to treatment
- Lack of treatment
- Significant decrease in immunity.
In chronic prostatitis, the inflammatory process in the tissues of the prostate gland is not expressed, so the symptoms may not be felt until exacerbation occurs.
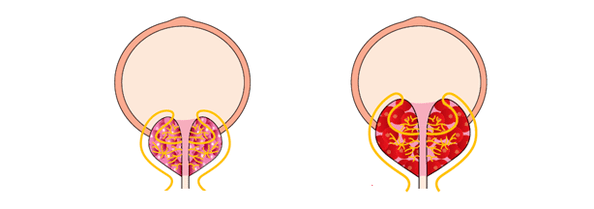
Another peculiarity of chronic prostatitis is that the primary inflammation of the prostate causes a deterioration in the innervation of the organ, which negatively affects its work and can cause autoimmune processes. During these processes, the immune system produces antibodies against the tissues of the prostate. Even after the infection has stopped, such prostatitis progresses.
Causes of non-infectious prostatitis
Non-infectious, i. e. , congestive prostatitis, occurs due to congestion in the pelvic area. It is most often chronic, gradually, developing over time, intensifying symptoms. This form of prostatitis is the most common.
What causes prostatitis in men in most cases? The main reason is the violation and stagnation of blood circulation. As a result, the body does not receive enough nutrients and oxygen, there is no complete outflow of secretions, ie favorable conditions appear for the development of inflammation. This condition usually occurs in less active men, less frequently in the background of trauma.
Causes of stagnant prostatitis
- Lack of physical activity
- Work at the long table, sitting, driving,
- Irregular sex life
- Constipation
- Overweight,
- An unbalanced diet
- Often a subdued urge to urinate
- Smoking and alcohol consumption
- Low back injuries
- Characteristics of the structure of the organs of the urogenital system.

All of these causes have a negative effect on blood circulation, both locally and in general. For example, smoking and regular alcohol consumption greatly weakens the tone of blood vessels, which impairs blood flow throughout the body. The prostate also suffers from this. Stagnation of pelvic organs affects men who do sedentary work as well as those who spend a lot of time in the car or are used to passive relaxation on the couch. A long session is usually not good for men’s health at all. One way or another, the blood vessels that supply the pelvic region become trapped and supply the prostate worse.
An unbalanced diet leads to deterioration of the general condition of the body, overweight and poor bowel function. All this also adversely affects the state of blood circulation, especially in the organs of the urogenital system.
Sex life is very important for men’s health, it needs to be regular. Having sex three times a week is considered average, but each has its own characteristics that depend on a man’s physique, desires, and needs. Insufficient sexual activity leads to stagnation, as the inevitably accumulating tension does not get discharged. Not only does blood stagnation occur, but also the secretion of the prostate in which harmful substances accumulate.
Excessive sexual activity is also harmful, as it takes a lot of strength away from the man, leading to physical and nervous exhaustion, hormonal imbalances. All this becomes a factor in the inflammation of the glandular tissues.
A sedentary lifestyle is one of the most common causes of prostatitis in men. Today we move a lot with traffic, we go up to the upper levels by elevator, they have done a lot to make our lives easier. However, the human body, especially the male, is designed for great physical activity. To get this, men have to play sports. You can always choose what you love, which is a pleasure. The daily gymnastics, which consists of simple exercises and walks, achieves good results.
Anatomical features of blood vessels or other structures in the pelvic region can lead to prostate congestion. These properties can be acquired as a result of congenital disorders or disorders, as well as trauma or other diseases. Violation of tissue structure, condition of blood vessels, development of cysts or tumors very often leads to significant changes in the function of both the organ and the arteries and veins that supply blood.
When to worry
If a man feels that he has problems urinating, starts going to the toilet more often, is worried about pain in the lumbar region, the groin, he should see a urologist. Even if the manifestations are minor, they should not be ignored. The appearance of such symptoms indicates that adverse changes have occurred in the body.

In case of urinary problems, groin and low back pain, consult a urologist!
Diagnosis and treatment
The causes and treatment of prostatitis are closely related, so a complete diagnosis is needed to successfully combat the disease.
Diagnostic procedures
- Collection of medical history,
- Rectal digital examination,
- Ultrasound,
- Bacteriological analysis of prostate secretion,
- Blood and urine tests,
- Analysis to determine PSA levels.
These procedures provide a picture of the condition of the prostate, making it possible to identify inflammation and its causes. PSA levels are required to rule out adenoma and prostate cancer. Repeated such analysis is required to monitor treatment success.
Prostatitis should be treated in a comprehensive manner, including the following methods:
- drug therapy,
- massage,
- physiotherapy,
- physiotherapy.
Depending on the cause of the disease, medications are prescribed that eliminate the infectious component, improve blood circulation, the outflow of urine and glandular secretions, and relieve cramps. The earlier you start treatment and the more responsibly a man treats him, the better the outcome will be.
However, for optimal prevention of the disease, it should not be treated. Preventing men from avoiding causes and provoking factors, a healthy lifestyle and sexual activity.
























